WHAT IS A MARINE PARK?
Marine Park is a sea zoned area that spans for a distance of two nautical miles from the lowest sea level, except in Kapas Island in Terengganu, Kuraman Island, Rusukan Besar Island and Rusukan Kecil Island in Labuan. These areas are zoned for a distance of 1 nautical mile from the lowest sea level.
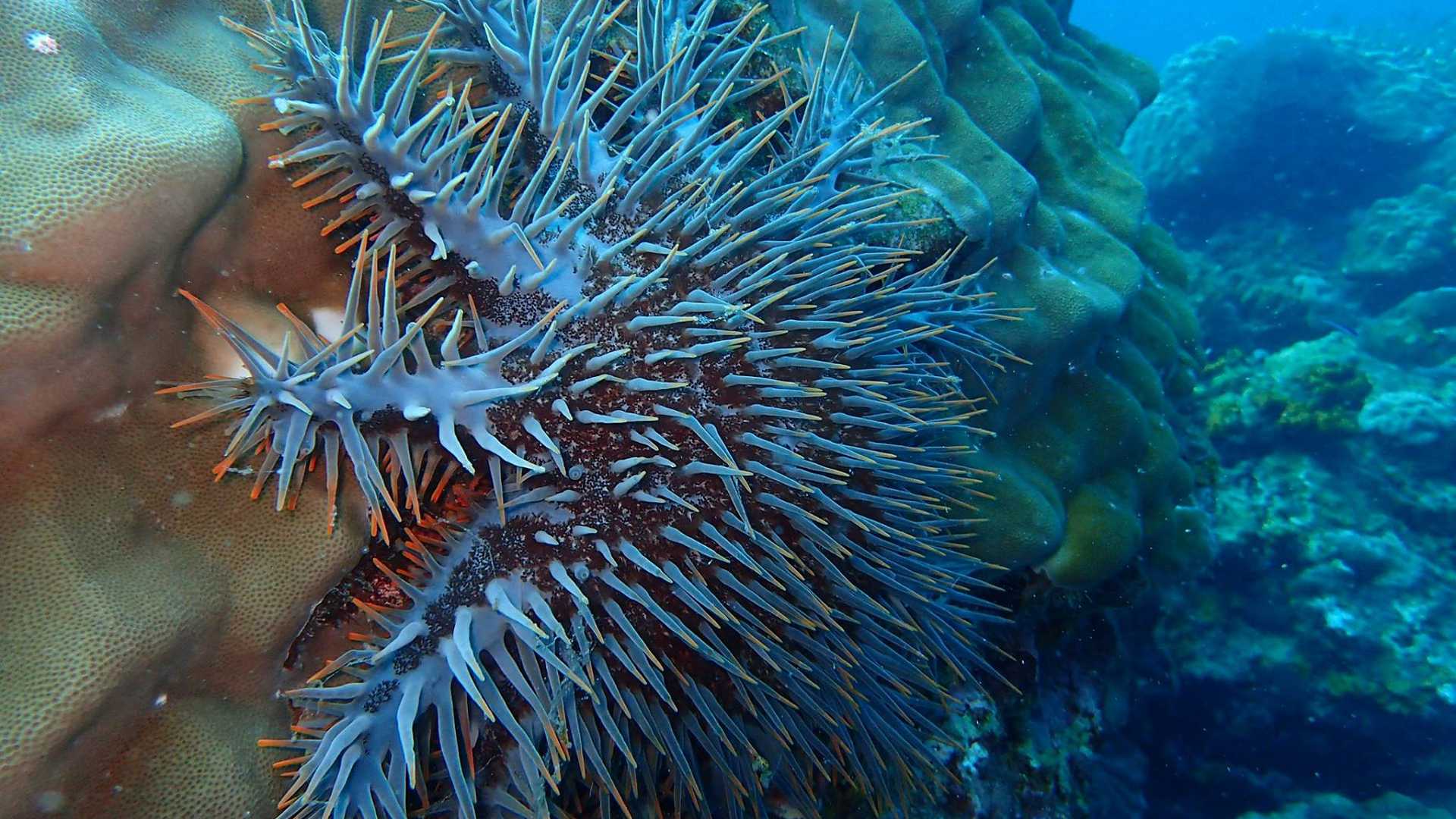
Marine Parks have been established to protect and conserve various habitats and aquatic marine life. All activities damaging coral reefs and marine ecosystems are prohibited and illegal under the Fisheries Act 1985.
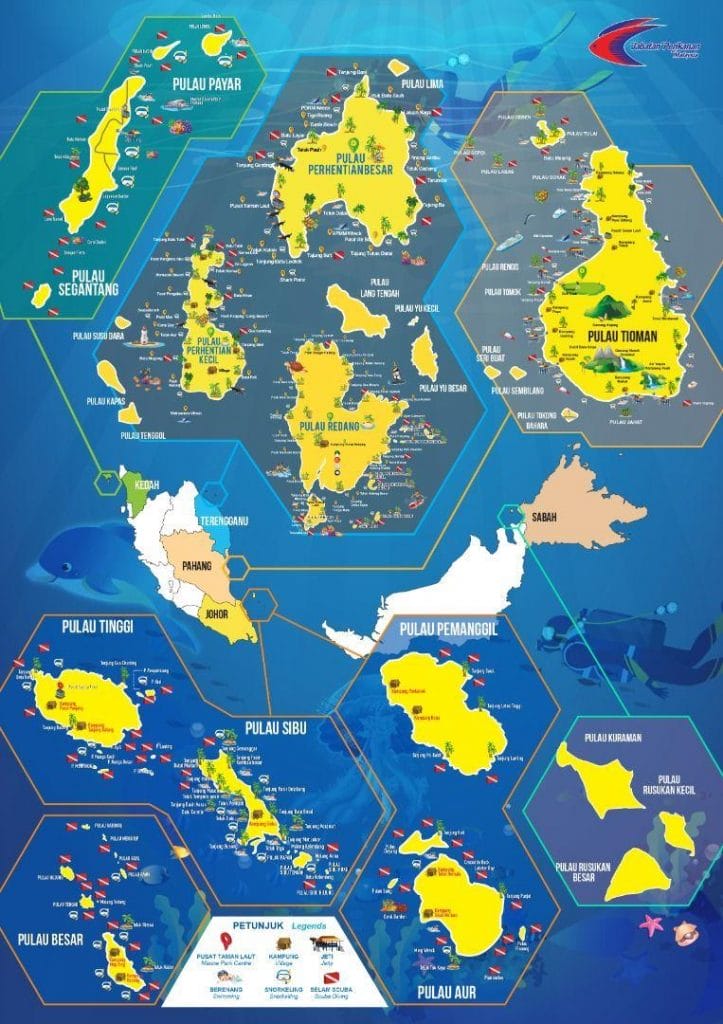
Today, the waters around Malaysia’s 42 islands are gazetted as Marine Parks.
Maintaining fishery resources:
- Coral reefs are important breeding grounds, food sources and habitats for important commercial fish. In Malaysia, 30% of the fish caught depends on coral reefs. The conservation of coral reefs indirectly helps the fisheries sector, protects fishermens’ jobs and ensures the continuity of food supply.
Maintaining biology diversities:
- Coral reefs are the richest marine ecosystems. The threat to coral reefs has a serious impact on the biodiversity of the world.
Protecting our waters:
- It serves as a barrier against coastal erosion from waves. 70-90% of wave energy is absorbed or deflected when it hits a coral reef. Dead or broken reefs will fertilise the beach and replace the sand that is washed away by the sea water.
Ecotourism resources:
- Become a source of attraction for scuba divers and snorkelers to explore the beauty of coral reefs. Good management and monitoring will preserve coral reefs as a sustainable source of ecotourism.
Food supply guarantee:
As a guarantee of food supply and sustainability of the fishing industry.
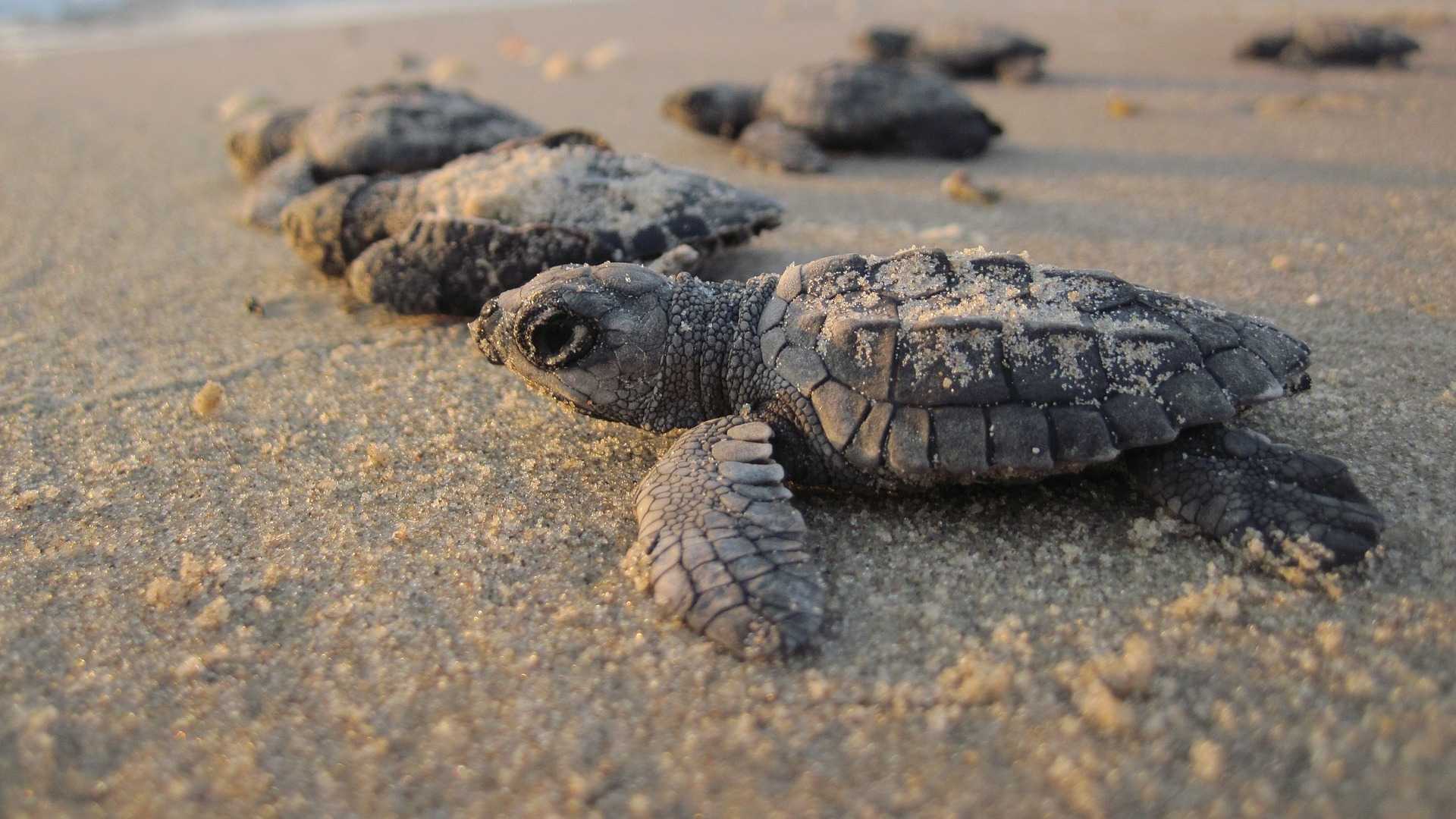
- Provides special protection to aquatic flora and fauna, protects, preserves and manages natural breeding sites and aquatic life habitats with special attention to unique, hard-to-find or endangered species of flora and fauna
- Provides opportunities and increases the survival rate of endangered aquatic life
- Encourage scientific study and research
- Maintain and increase the productivity and natural conditions of the ecosystem
- Regulate recreational activities and other activities to prevent the occurrence of continuous damage to the marine environment
- Classify Marine Park Waters into zones for the purpose as specified in paragraphs (1) to (5) above
PROHIBITED ACTIVITIES
Marine Parks are marine protected areas whereby activities that can damage coral reefs and their ecosystems are strictly prohibited and illegal under the Fisheries Act 1985. Such activities are:
- Taking, capturing or interfering with any marine resource whether alive or dead
- Carry out any type of water sports activities using high power boats
- Anchoring anchors in coral reef areas
- Step on or touch coral reefs
- Polluting or disposing any contaminants
- Own or use any fishing gears
- Building any structure in the waters of the Marine Park
- Carry out diving or snorkeling activities in the boat passage area
- Collecting corals, shells and marine organisms (either alive or dead)
ALLOWED ACTIVITIES
While in the Marine Park area, only activities that do not damage the coral reef and its surroundings can be done. The activities are:
- Diving
- Snorkelling
- Underwater photography
- Water recreational activities such as kayaking
Coral reef is:
- A living organism that looks like a jellyfish, under the group Cnidaria.
- Consists of two groups:
- Hard Coral
- Soft Coral
- Symbiosis with zooxanthellae produces Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) which forms coral.
- Coral eats at night using tentacles to catch food
- Reproduction: sexual and asexual (binary fission)
- Growth depends on type of coral:
- Slowest (0.5 cm per year) e.g: Massive Coral
- Fastest (10 cm per year) e.g: Branching Coral
- Growth rate is affected by environment factors
- Types of coral growth:
- Foliose
- Massive
- Columnar
- Branching
- Free living
- Tabulate
- Encrusting